Overview
Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. The electric and magnetic fields that compose the light wave constantly oscillate transversely to the propagation direction; the polarization describes the direction in which these electromagnetic fields oscillate.
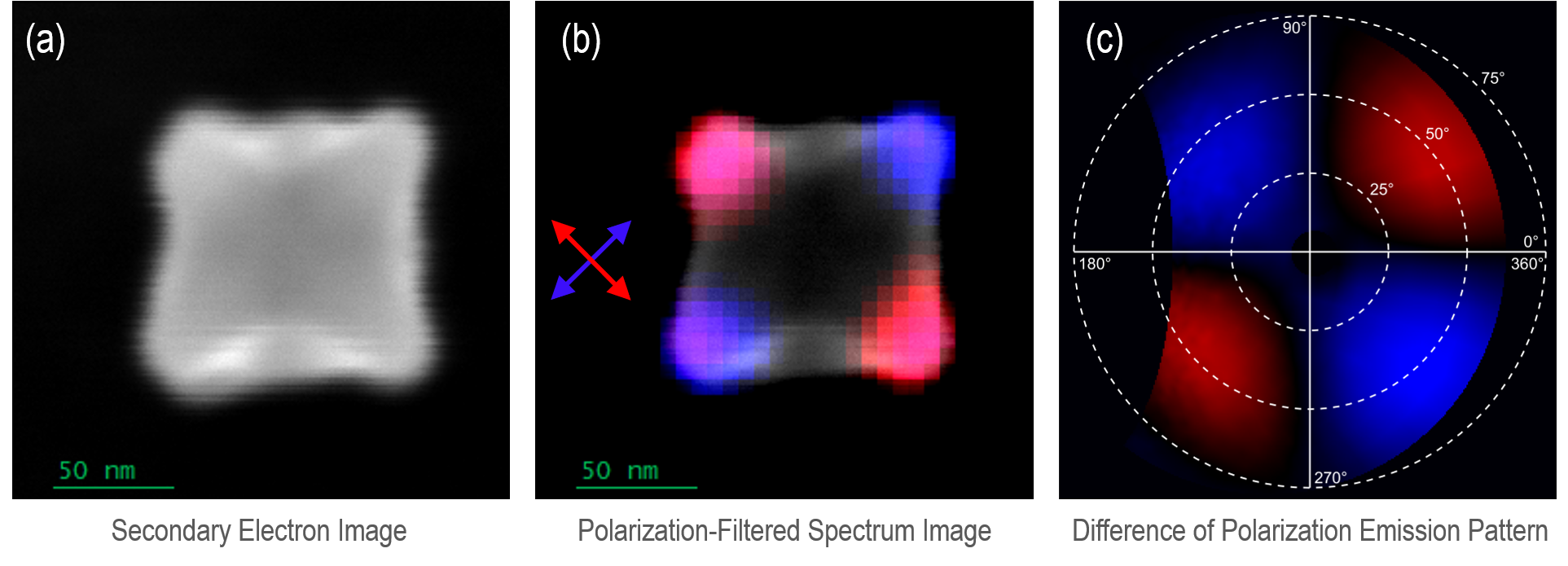
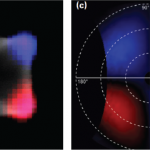
A polarization analyzer can be incorporated into the optical chain of another cathodoluminescence (CL) mode to provide polarization-filtered or polarization-resolved data, such as a polarization- and wavelength-filtered map or a polarization- and angle-resolved emission pattern (polarimetry).
Data collection
Polarization filtered: The polarization analyzer consists of a linear polarizer with a user-defined orientation.
Polarization-resolved: The polarization analyzer consists of a quarter-wave plate and linear polarizer. When images are captured over six different analyzer settings, the Stokes parameters that describe the full polarization state of the emitted light may be retrieved.
Uses
Polarization plays a key role in light-matter interactions and helps study coherence, scattering, birefringence, and chirality, finding wide applications in nanophotonic applications. More recently, the degree of polarization has been used to characterize strain in single-crystal semiconductors and insulators. While in (multi-crystalline) samples such as meteorite thin sections, the polarization of the emitted light has also been used to reveal crystal orientation and mineral texture.